Podcast: Episode 28, how to choose your sunscreen?
Listen to the audio episode to help you choose your sunscreen
- Available on: Episode 28: How to choose your cream?
- Also available on Spotify , Apple Podcast and Google Podcast
Choose your solar product:
- SPF = UVB protection
- The circled UVA logo = UVA protection
- Claim "resistant" or "very resistant" to water
- Texture: avoid aerosols
CHOOSE YOUR SOLAR PRODUCT
During the summer, it is all the more necessary to use a sunscreen product to limit the damage of the sun on the skin. But how do you choose the right sunscreen product? What are the criteria to consider when buying?
WHAT IS SPF?
The SPF corresponds to the Sun Protection Factor , or the sun protection factor. It is a number greater than 1 that characterizes the ability of a product to protect the skin from UVB rays . As a reminder, UVB rays are responsible for sunburn (B for burning). 🖇 See episode 27 for more details on UV. Sun products never completely protect, they limit the damage caused by the sun.
A sunscreen product must have an SPF of at least 6.
The SPF is therefore a claim made by sunscreen products to quantify their protection and allow consumers to make an informed choice. This is the selling point of the most effective solar products
HOW TO INTERPRET THE SPF NUMBER?
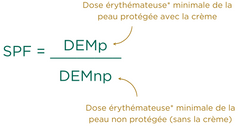
The SPF corresponds to the smallest dose of sun triggering sunburn on skin protected by the cosmetic divided by the smallest dose of sun triggering sunburn on unprotected skin.
The scientific terms are MEDp for Minimal Erythematous* Dose to Protected Skin and MEDnp for Minimal Erythematous* Dose to Unprotected Skin.

*an erythema is a redness of the skin that disappears when you press on it (like a sunburn)
Example: If the skin reddens after 10 mJ/cm² without protection, then it will take an exposure of 300 mJ/cm² to make it red with an SPF 30.
Example 2: considering the constant rays of the sun: If the skin reddens after 10 min without protection then it will be protected for 10 x 30 = 300 min = 5h with an SPF 30.
Please note that these are theoretical calculations. In fact, the cream is removed with rubbing, bathing, etc. It is therefore necessary to reapply it every 2 hours or after each bath when exposed.
HOW DOES MY SUN PRODUCT FILTER UVB?
We can illustrate the measurement of SPF in terms of the duration of exposure before blushing , but we can also think of it as the filtration of UVB . An SPF 2 corresponds to a protection that allows us to double our exposure time before blushing, we can also see it as a 50% filtration of UVB.

And so, an SPF 10 corresponds to a filtration of 90% of UVB, an SPF 30 corresponds to a filtration of 96.67% of UVB and an SPF 50 is a filtration of 98% of UVB.


WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE IN PROTECTION BETWEEN SPF 30 AND SPF 50?
- An SPF 30 filters 96.67% of UVB rays, ie it allows 3.33% of UVB rays to pass through.
- An SPF 50 filters 98% of UVB so it lets only 2% of UVB through.
Presented in this way, the protections of SPF 30 and SPF 50 do not seem so different. But ... the ratio between the UVB rays that SPF 30 passes over those of SPF 50 seems much greater.
3.33/2 = 1.67 = 167%
therefore, with an SPF 30, your skin receives the equivalent of 167% of the UVB received with SPF 50 protection. That is 67% more UVB received with an SPF 30 than with an SPF 50 .
It's up to you how you want to anticipate sun protection: do you consider the UVBs that pass or those that are blocked? We can make the analogy with the sales: when the article has a generous reduction of 70%, do you think of the 30% to pay or the reduction of 70%?
⚠️ Beware of certain errors on social networks: an SPF 30 does not allow 167% of UV rays to pass! Because ...
- it is not possible to let through more UV than there is initially (100%). Except if the solar products multiplied the amount of UV received. What would be worse than not putting anything. The product cannot therefore allow more than 100% of UV rays to pass through.
- the calculation is misinterpreted. An SPF 30 filters 96.7% of UVB so it lets through 3.3%, which corresponds to 167% of the amount let through by an SPF 50. That is a 67% increase in rays that damage your skin and more with an SPF 30 rather than an SPF 50. It's the same ratio between 50 and 30.
💡 Choose your SPF according to your phenotype, sunshine and also your exposure.
HOW IS SPF MEASURED?
The SPF is determined on human volunteers , so it is an in-vivo test. The natural protection of the volunteers' skin matters in determining the SPF, so only fair-skinned volunteers should be chosen.
Concretely, the volunteers receive precise quantities of irradiation, then the erythema is evaluated the next day. Thus, it is possible to determine the MED, Minimum Erythematous Dose with and without protective cream, and therefore evaluate the SPF.
WHICH CREAM TO PROTECT YOURSELF FROM PHOTOAGEING?
Photoaging is mainly due to UVA rays . However, an SPF protection claims UVB protection only.
To make sure your creams are protecting your skin from UVA rays, look for the circled UVA logo or the claim “broad spectrum” in English. These standards state that UVA protection should be at least one third of the SPF .

Example: if the product claims an SPF 30 and the circled UVA logo, this means that it protects the skin 30 times longer from UVB and 10 times longer from UVA compared to skin without protection.
HOW IS UVA PROTECTION MEASURED?
There are several methods standardized by ISO standards: the in vivo test (ISO 24442) which is based on Meirowsky pigmentation and the in vitro test (ISO 24443) which calculates the critical wavelength λc.
The in vivo test for determining protection against UVA is almost the same as that for UVB, except that we do not observe redness (sunburn) after exposure but Meirowsky pigmentation , which is the gray-blue coloration that develops during UVA exposure. This color is characteristic of the photo-oxidation of the colorless precursors of melanin.
This method is reproducible, but the reaction occurs only on dark skin, and does not allow testing of colored products.

The in vitro test makes it possible to determine the critical wavelength λc of the absorbance when the product is spread on a PMMA plate. This mathematical measurement assesses a product's ability to protect against the highest wavelengths. λc must be equal to or greater than 370 nm.

DOES MY CREAM PROTECT ME AFTER SWIMMING?
Some sunscreen products can also be considered water -resistant or very water-resistant . These claims ensure their good hold after a swim.
There are no ISO standardized in vivo methods for measuring product water resistance, which can lead to large differences in measurement from one laboratory to another. Here again the regulations are different from one country to another.
In general, the in vivo test is done on volunteers after they have spent 40 min (resistant) or 80 min (very resistant) in water .
In Europe, cosmetics must have UVB protection after swimming greater than half of their SPF to be labeled water resistant or very water resistant. Whereas in Australia it is more difficult because the cosmetic must remain in the same SPF category for this claim.
WHICH TEXTURE TO CHOOSE?
The texture you like and will reapply enough is the right texture. I do not recommend aerosols because we tend to use less and therefore protect ourselves less well.
Ratings
PENSÉ-LHÉRITIER AM, Design of cosmetic products: Formulation . 2016. Lavoisier, Paris.
MAGAND CASTEL J, Podcast: Episode 27, 10 solutions to limit photoaging . 2022. Available at: https://mastelcosmetics.com/blogs/podcast/episode-27
Did you like this article? 📌 Pin it on Pinterest to find it later!
 |
 |
 |







Leave a comment